
IoT and Smart Packaging
Inovum’s founder and CEO Franz Inselkammer spoke to Victor Borras, Chief of Marketing at Knauff Industries about the future possibilities of intelligent packaging.
Listen to the full podcast here (Podcast language Spanish) or continue reading to learn more about this exciting topic.
What is Smart packaging?
Smart packaging is a new tendency that connects the physical with the digital world. It refers to technology embedded into packages with the main benefits of improving the customer experience and reducing costs.
There are 2 types of smart packaging: active packaging and intelligent packaging. Active packaging is packaging that improves the end-user experience. A typical example would be a sticker on a food product that turns red when the product is expired. Intelligent packaging goes beyond the mere packaging task. It refers to packaging that uses sensors and other devices, for instance, to track a product, sense an attribute of the packaged item or its environment (e.g., humidity, temperature, CO2 level, pressure, etc), and communicates this information to the user (e.g. the manufacturer).

The last mile delivery challenge
The last mile delivery refers to the las step of a delivery process which is the delivery from a transportation hub to the final recepient (usually a personal residence or retail store. It is the most expensive and most critical part of the whole delivery process.
It is easy to deliver a parcel to a transportation hub or warehouse. The real challenge is the last mile, that is, getting the parcel to the final customer.
Last mile shipping can account for 53% of a shipment’s total costs. The main challenges are remote delivery address locations, incorrect or addresses, lack of proper signage, unpredictability in transit, high traffic in cities, street closed or deviations, human errors, or customer not at home, etc. Further, it is important to evaluate factors like the size of the packaging. Is the product fragile? Does the product need refrigeration? Can the product by delivered by bike or is a refrigerated van necessary?
Companies need to address these challenges at the earliest because the delivery landscape is changing rapidly. In some countries, for instance, drone deliveries are already a reality.
Drone delivery in Spain. Where do we stand?
In several countries around the world, drones are already being used for time-sensitive deliveries. Amazon, Uber, and Google are all vigorously working on bringing their products to the sky. Uber Elevate, Amazon Prime Air and Google Wing are the names of their future delivery drone systems.
In France, drones are already used to deliver parcels to remote areas in the Alps. In Ireland MannAereo drones are used to deliver food and in other countries like the Iceland, UK, Croatia and Finland, drone deliveries are currently being tested.
In Spain the body responsible for regulating the use of drones is the Spanish Agency for Aviation Safety (AESA). The Spanish Royal Decree that currently regulates drone flights will remain in force until 1 January 2022. During 2021, a new Royal Decree is expected to be published to regulate drone flight in Spain and update the current regulations regarding the European regulation.
Currently restrictions for flying drones in Spain include:
- The drone, must always stay within visual range of the pilot (except in specific category under STS BVLOS).
- Never exceed 120 m in flight.
- Do not fly in a minimum of 8 km from any airport, aerodrome or controlled airspace.
- Liability insurance is not mandatory, but it is highly recommended to have one. The pilot will be responsible for any damage caused by the aircraft.
- The drone must have a fireproof identification plate fixed on the structure that will contain data such as the manufacturer’s name, model, serial number (if applicable) and the pilot’s contact details.
- Protect the right to privacy of individuals who may appear in the images captured by the drone, and take special care with their public disclosure in order not to violate the Data Protection Act.
The ENAIRE Drones website is an official platform that provides all to fly your drone safely in Spain.
Examples of smart packaging
Product authentication and brand security
Thanks to microchips embedded in products, scanners can verify the authenticity of a product. This is especially helpful for brands facing counterfeiting issues. Companies such as MK, Channel, Louis Vuitton and Levi’s have already started implementing smart packaging to ensure consumer protection and protect their brand reputation.
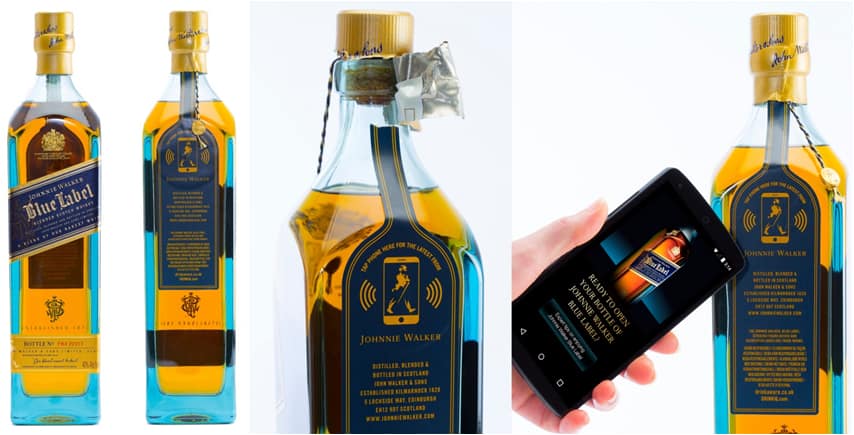
Sensors to control package handling
Some types of smart packaging can record whether a product has been opened or tampered with. Thin film, for example, has been used by Johnnie Walker in “connected” NFC bottles. Consumers can scan the bottles and determine if the product is properly sealed.

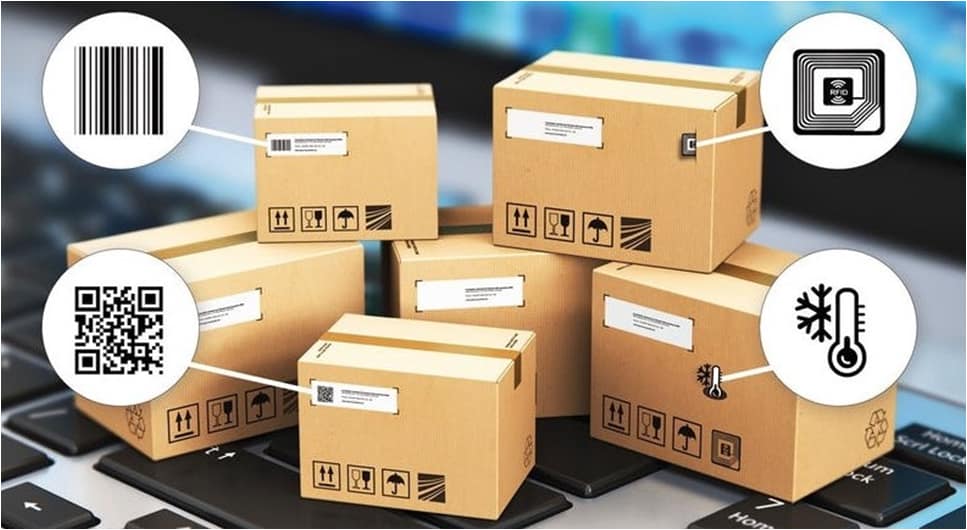
Tracking records (Barcode, RFID …)
Smart products retain a fingerprint at every step, from production to retail. Tracking records allow access to the life cycle of each SKU, showing where it has been, how and when it has changed hands, etc. This allows companies to more easily identify errors or problems throughout the supply chain.
Environment sensors (temperature or humidity)
Since some products are sensitive to environmental changes, NFC stickers with temperature sensors can track these changes. Scanning the item allows consumers to determine if an item has been kept at its optimum temperature.
Automatic orders in case of shortage
Smart packaging can allow consumers and retailers to automatically reorder products when the stock is running out by connecting to stock data on the shelves or providing triggers on the products themselves.
Digital labels
A digital label allows consumers to access all the information about a product instantly. Through a QR code or other activators, consumers can access videos, images or any other relevant information. In a food product, for example, you can access recipe suggestions and video tutorials.
Comments are closed.